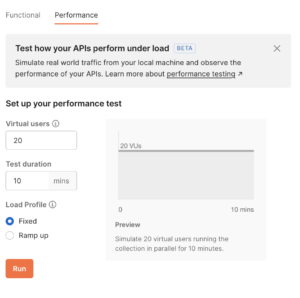
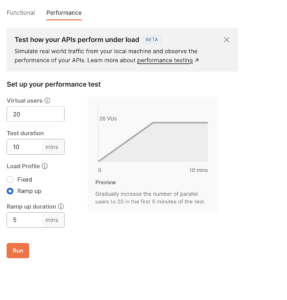
Newman is a command-line tool that allows you to automate the execution of Postman collections.
Postman is an API development environment that enables you to design, test, and document APIs.
Newman comes in handy when you want to run your API tests in a Continuous Integration (CI) pipeline or automate API testing.
To get started with API automation using Newman, follow these steps:
1. Install Node.js and npm:
Ensure you have Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) installed on your machine. You can download the latest version from the official Node.js website.
2. Install Postman and create a collection:
If you haven't already, download and install Postman from the official website. Then, create a collection and add API requests with associated test scripts to it.
3. Export the collection:
Once you have created and saved your collection in Postman, export it as a JSON file. This file will contain all the API requests, test scripts, and other relevant information.
4. Install Newman:
Open your terminal or command prompt and install Newman globally using npm:
```
npm install -g newman
```
5. Run the collection with Newman:
In your terminal, navigate to the directory where you saved the exported collection (JSON file) and execute the following command:
```
newman run your_collection.json
```
Replace `your_collection.json` with the actual name of your exported collection file.
Newman will execute each request in the collection and display the results in the terminal.
6. Writing test scripts:
If your collection has test scripts, Newman will run them automatically. You can write test scripts using JavaScript in the Postman collection. These scripts allow you to perform various validations on the API responses and make sure they meet the expected criteria.
7. Using Newman in CI/CD pipelines:
To incorporate Newman into your CI/CD pipeline, install Newman on the build server and run the collection as part of your test suite. This helps ensure that your APIs are tested automatically whenever changes are made to the codebase.
Summarization
Newman provides various options for generating reports, controlling iterations, and handling environment variables during the test run. You can explore the official Newman documentation for more advanced features and customization options.
Remember to keep your collection and test scripts up to date as your API evolves. Regularly update your tests to reflect the latest changes and ensure that your API remains functional and reliable.